Table of Contents
You may have noticed more spam in your inbox lately.
One major spam cause is senders not properly employing email authentication, leaving room for spammers to invade inboxes for phishing schemes.
So, Google and Yahoo have introduced new requirements to reduce spam and protect recipients from malicious messages.
While designed to combat spam and phishing, these standards may hurt your email outreach campaigns if you fail to comply.
Not to worry, we’ve compiled a detailed — yet simplified — guide for link builders and digital PR professionals to help navigate these new standards and make it into your prospect’s inbox.

TL:DR Summary
Don’t have time for the full article?
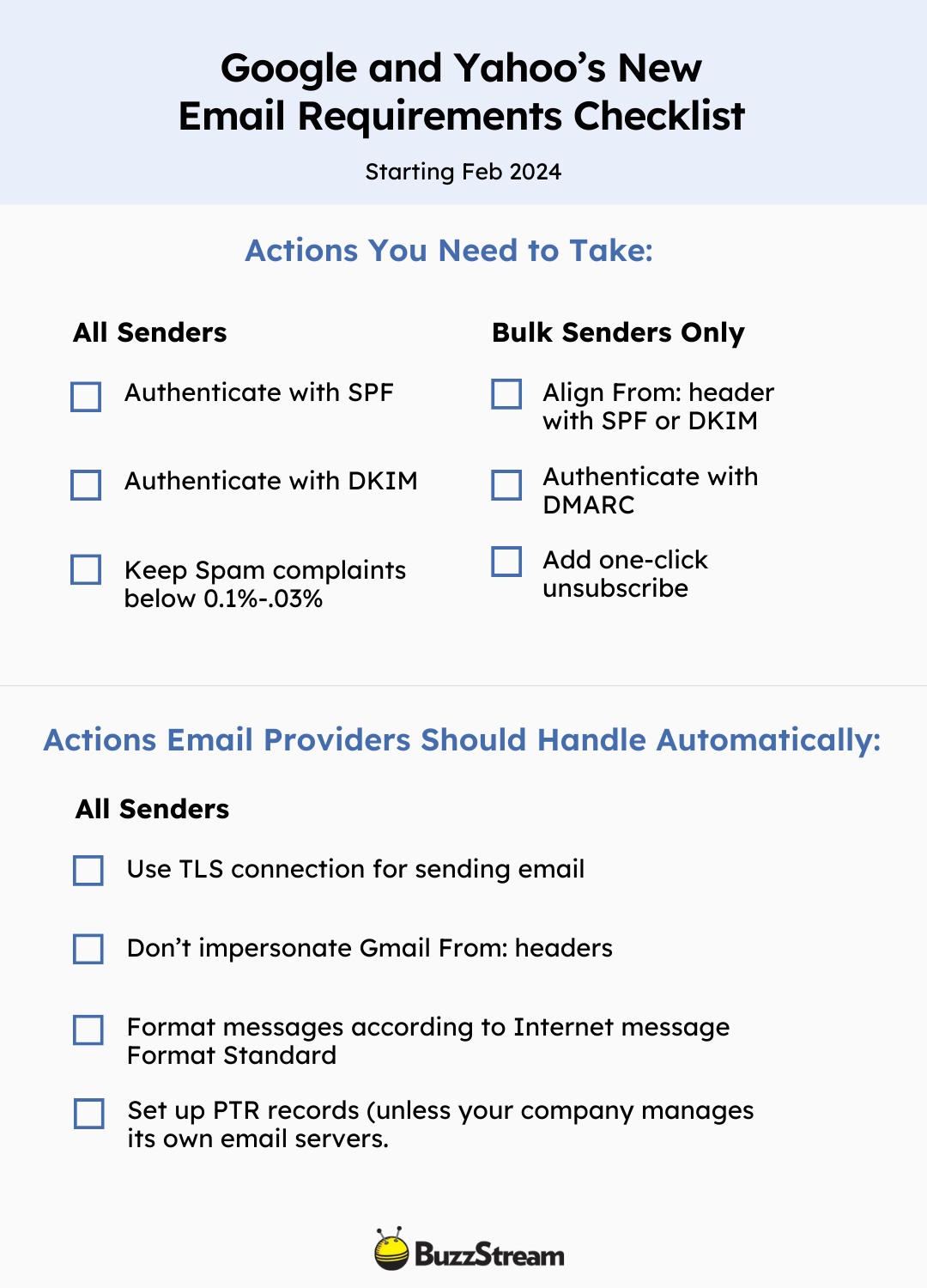
The quick summary is that Google and Yahoo’s new email standards will be effective starting February 2024. All email senders sending to personal Gmail accounts, especially those sending over 5,000 emails within 24 hours, must implement specific authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) and user-friendly practices like one-click unsubscribe links. Also, Spam rates must be kept at 0.1% to 0.3%.
Non-compliance will lead to email rejections and damage your sender’s reputation.
Who Do The Rules Apply To?
The new set of rules applies to two types of senders, one set impacts all email senders and additional requirements for those sending more than 5,000 emails, aka “bulk senders,” to Gmail accounts within 24 hours.
The 5,000 email limit applies to messages from the same domain — not individual email addresses.
When Do The New Rules Go Into Effect?
The rules begin in February 2024, but not for everyone. The requirements are broken down by bulk sender and all senders.
We’ve broken the dates down below:
Enforcements will be implemented in phases for bulk senders. (There is currently no date for non-bulk senders yet.)
February 2024 – There are no major penalties at the start. Bulk emailers will get temporary errors on a small percentage of emails they send that don’t meet the requirements.
Google will notify the sender of the error (along with an error code).
According to Google’s documentation, these messages are intended to help identify email issues “so that senders can resolve issues that result in non-compliance.”
April 2024 – Google will begin rejecting a percentage of bulk senders’ emails that don’t meet the guidelines. They’ll gradually increase the rejection rate over time.
June 1, 2024 – Bulk senders must have implemented one-click unsubscribe. (BuzzStream has already built this into the product, so if you’re a BuzzStream customer, you won’t need to worry about this).
Non-Bulk Sender Effective Dates and Impact
If you’re not a bulk sender, we strongly recommend implementing the following authentication and spam monitoring as soon as possible.
Many of these changes will likely impact deliverability for all outreach email senders.
What Are the New Requirements and How to Comply?
The new requirements fall into four main categories:
- Authentication and security
- Minimizing spam complaints
- Making unsubscribe easy for recipients
- Formatting messages according to the Internet Message Format standard
Your mail provider will likely automatically cover most of the requirements, but some will not. We’ve marked down where you need to take action and where you don’t.
Authenticating and Sending Securely According to New Protocols
You may need help from your IT department, DNS provider, and mail provider.
Before you start, use this free tool to check if you meet Google’s SPF, DKIM, and DMARC (for bulk senders) requirements.
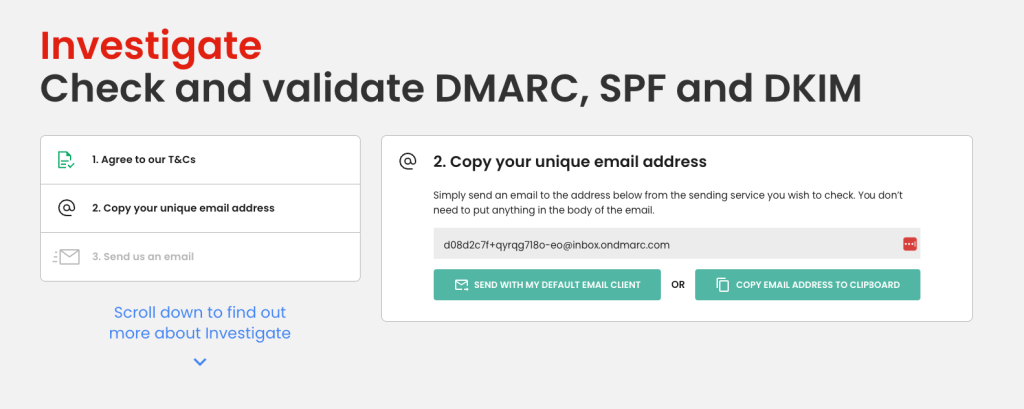
You can skip these first three checks if you meet SPF, DKIM, and DMARC (for bulk senders).
1. Authenticate with SPF
Create a record that lists the IP addresses and domains that can send email on behalf of your domain. Then, publish it to your DNS record.
How: Your DNS provider will have specific instructions for doing this (usually your domain registrar). Here is how to add an SPF record on Godaddy and Google.
2. Authenticate with DKIM
Publish a DKIM record in your domain’s DNS settings.
How: There are several steps to setting up your DKIM records and they will vary depending on the email provider and DNS provider. Examples – Google Workspace and Microsoft 365.
3. Authenticate with DMARC (only required for bulk senders).
You’ll prepare your DMARC record after setting up SPF and DKIM.
How: Setting up DMARC can be tricky, but several resources can help you with this.
First, you can use one of the many DMARC wizards to create your DMARC record. Once you’ve completed this, follow your DNS provider’s instructions to add or update a DNS TXT record. Again, you may need help from your IT department.
Don’t know what any of these acronyms mean? Jump to the terminology section.
4. Set up PTR records
If your company hosts email with a mail service provider, this will already be handled for you. If your company manages its email servers, you must ensure that your sending domains or IPs have PTR records.
How: Check with your IT department to see if your company manages its email servers.
5. Use a TLS connection for sending email
If you’re using a reputable email service provider, it’s very unlikely that you need to worry about this.
How: If you’re managing your mail servers or unsure if your mail provider does this, you should check with the IT team or the mail provider.
6. Don’t impersonate Gmail From: headers
Gmail blocks messages that contain more than one email header of the same type because some malicious senders use them to impersonate legitimate senders.
If you’re using BuzzStream or another reputable platform, you don’t need to worry about this (BuzzStream follows the Internet Message Format standard).
How: Check with your outreach platform to ensure they follow the Internet Message Format. If your platform does not comply, we recommend switching platforms.
7. Add ARC headers
If you regularly use mailing lists or inbound gateways, add ARC headers to outgoing email.
(This is unlikely to impact outreach professionals, as it’s primarily focused on mailing lists.)
How: While this is unlikely to impact your outreach if your company manages its own email servers, best practices are to make sure it’s implemented.
8. Align the domain in the sender’s From: header with the SPF or DKIM domain (only required for bulk senders).
This is required for direct mail to pass DMARC alignment.
How: You’ll do this as part of the DMARC setup process.
Minimizing Spam According to the New Guidelines
If you’re following best practices, you’re unlikely to encounter spam complaint issues. If you’re not, however, you’re likely to see significant deliverability impacts when this goes into effect.
9. Strive to keep spam complaints from personal Gmail addresses below 0.1%, and never let it exceed 0.3%.

How: To keep spam complaints to a minimum, we recommend the following:
- Sign up for Google Postmaster Tools and Yahoo’s Complaint Feedback Loop to check and keep track of your rates.
- Only send to someone who wants your email when you’re sending to a personal Gmail address. You can do this by building your own media list.
- Verify emails before sending them using our favorite digital PR tool for verification, called Neverbounce.
- Vet every prospect in your outreach list after you’ve found their email address to ensure they’re suited for your campaign. (If you’re using BuzzStream, the BuzzMarker can help you streamline this process and save time.)
- Personalize your emails; don’t just bulk-send canned templates. (Using BuzzStream, you can easily create templates and add spots for unique, custom text in every email you send.) Check out our email outreach templates for some extra resources.
- Set custom tracking domains. If you use open tracking or click tracking in BuzzStream, set up a “custom tracking domain.” When you do this, the URLs for tracking opens, and clicks will come from your domain instead of BuzzStream’s. (Here’s how to set up open or click tracking.)
- Don’t send to people who don’t respond to your emails after multiple outreach attempts. Watch how often you’re sending to contacts. (BuzzStream’s outreach history and filters display all previous connections and the dates you’ve last contacted them.)
- Warm up your email address when you get started and send emails at a steady rate (don’t blast emails at the same time). (Use BuzzStream schedules and throttling to ensure this happens.)
- Don’t send to email addresses that bounce. (If you email someone in BuzzStream and it bounces, we cancel the sequence.)
- Add an unsubscribe function, which is covered in the next section.
Simplifying Unsubscribe Actions For Users
Most email service providers should support this eventually, but it’s a question of when.
10. Add One-Click Unsubscribe links (only required for bulk senders)
Bulk senders must include a one-click unsubscribe link in the header of the email and a clearly visible unsubscribe link in the message body.
How: Depending on your email service provider (e.g., Gmail, Office 365), this may be something they support on their platform. We recommend asking them before April 2024. BuzzStream has already developed ‘one-click unsubscribe’ capabilities and will enable this for all customers before the June 1 deadline. If you’d like us to enable this now, please contact support.
You can add unsubscribe links to your message body everywhere in BuzzStream where you send emails; here’s how.
Formatting Messages According to the Internet Message Format Standard
Most email providers format their emails according to the correct standards.
11. Format messages according to the Internet Message Format standard.
How: There aren’t tools that help with this. Most reputable providers will format it correctly.
If you aren’t sure, ask your provider how they comply with the standard. If your answers aren’t satisfactory, we recommend switching providers.
If you’re using BuzzStream, you don’t need to worry about this—BuzzStream formats messages according to the standard.
To Recap:
What is BuzzStream Doing to Help Users With Google and Yahoo’s New Standards?
BuzzStream provides a range of built-in features that ensure your emails comply with these new Google and Yahoo guidelines and existing guidelines like the CAN-SPAM Act and GDPR.
One-Click Unsubscribe Feature
BuzzStream users can add a one-click unsubscribe functionality, ensuring compliance with the requirement for senders to provide an easy opt-out option for recipients.
Custom Tracking Domain Setup
By offering the option to set up a custom tracking domain, BuzzStream ensures that email tracking URLs align with the user’s domain, enhancing email deliverability and sender reputation.
Email Format Standard Adherence
BuzzStream formats messages according to the Internet Message Format standard, which is crucial for meeting Google’s and Yahoo’s requirements.
Prospect Vetting with BuzzMarker
BuzzMarker makes it easy to manually vet your prospects during prospecting, reducing the likelihood of spam complaints.
Personalization of Emails
BuzzStream’s template features allow for customization and personalization of emails, reducing the risk of emails being marked as spam and improving engagement.
Managing Outreach History and Frequency
BuzzStream tracks previous interactions and last contact dates, helping users avoid over-sending and maintaining a healthy sender reputation.
Bounce Management
BuzzStream automatically handles bounced emails by canceling sequences, thus maintaining list hygiene and sender reputation.
How Will This Impact Link Builders and Digital PR Professionals?
All of the spam guidelines are for sending to personal emails, so unless you send to personal Gmail and Yahoo addresses often, this likely won’t impact digital PRs and link builders as much as email marketers.
However, this doesn’t mean these new standards won’t soon apply to all email sending – business emails included. So, it’s important to work best practices into your outreach now.
On the technical side, you need to make sure you authenticate. That’s a given.
On the outreach side, it’s about keeping your emails from getting marked as spam when sending to personal gmail accounts.
If you’re not vetting prospects and contact info sending to irrelevant addresses, you’ll most likely get in trouble. Stick to white hat link building.
For example, there are a lot of sites that have at least one Gmail address (e.g., sitename@gmail.com). Using a scraper tool to grab email addresses and send without verifying, you will hit a personal email address. So, you are putting yourself at risk.
We know sending outreach at scale is a big part of the strategy for many agencies, link building and digital PR alike, but these standards may signal a need for change in how we operate.
Terminology to Know
We know there is a lot of fancy jargon involved with these requirements. All of the terminology used is explained simply below:
- SPF: Sender Policy Framework is an authentication protocol that prevents spam by verifying if incoming emails come from a valid server listed in the domain’s DNS records.
- DKIM: DomainKeys Identified Mail is an email authentication technique that prevents spam by adding a digital signature to outgoing messages. This allows the receiver to verify that the email is from an authorized domain (and not a phishing attempt).
- DMARC: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, & Conformance builds on top of SPF and DKIM to provide the most robust safety mechanism for the emails you send. It requires emails to pass SPF and DKIM authentication as well as SPF and DKIM “alignment” (i.e., the domain for the address in the “header-from” field has to match the “envelope from” domain listed in the SPF record and the “d=domain” field in the DKIM signature.
- TLS: Transport Layer Security is a communication protocol that encrypts emails to ensure secure communication.
- ARC headers: Authenticated Received Chain headers indicate the message was forwarded and identify you as the forwarder.
- DNS: The Domain Name System operates as the phonebook for the Internet, and it helps get traffic to the right location. DNS is a list of domains (e.g., companyname.com) and the unique IP addresses for each domain.
- Sender Reputation: A score that each Inbox Service Provider has for your mail domains. The better the sender score, the more likely your emails will be delivered. There are several ways to check your sender score, including Sender Score.
Frequently Asked Questions from BuzzStream Customers
Here are some questions we’ve received in the chat or support emails.
How Do I Check My DNS Records to Ensure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Are Added?
You can easily use a tool like RedSift to check if SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are added.
What if I Send Less Than 5,000 Emails Per Day?
If you send less than 5,000 emails daily to personal Gmail addresses, you must only adhere to the requirements above marked “All Senders” for now.
However, the bulk sender requirements may soon be applied to all senders, so we recommend working towards implementing all of them sooner rather than later.
Do The Requirements Apply To Me If I Send 5,000 Emails Per Day Total From Different Email Addresses?
The bulk sender requirements apply to those sending 5,000 emails from the same domain.
So, if you sent 2,500 emails to personal Gmail accounts from vincent@buzzstream.com and 2,500 from steve@buzzstream.com, technically, you are a bulk sender.
But, if you send 2,500 emails from vince@buzzstream.com and 2,500 from a personal Yahoo address like vince@yahoo.com, technically, you aren’t a bulk sender.
Either way, if you send many emails, you will want to work towards enabling the proper authentication, security, and spam requirements.
What Happens if I Fail to Comply?
In short, if you fail to comply, your emails will not get delivered, and worse, your sender reputation will be tarnished, severely impacting overall deliverability.
But, Google has set a sliding scale of repercussions for noncompliance. Starting February 2024, bulk emailers not meeting Google’s new requirements will initially face temporary errors on some emails, with Google providing error notifications for resolution. By June 2024, Google will progressively increase email rejections for non-compliance.
Do Email Sender Rates Impact SEO Rankings?
Email sender rates don’t directly affect SEO rankings. Still, non-spammy email campaigns can indirectly boost SEO by driving more traffic to your website and increasing brand awareness, potentially leading to higher search engine visibility. Effective email marketing can also enhance user engagement and content distribution, positively contributing to SEO metrics.
Have any other questions? Reach out to us in the chat or email us at support@buzzstream.com.
 Check out the BuzzStream Podcast
Check out the BuzzStream Podcast